Installing, removing, and updating packages is a typical activity on Linux. Most of the Linux distributions provides some kind of package manager utility. For example, apt-get, dpkg, rpm, yum, etc.
On some Linux distributions, yum is the default package manager.
Yum stands for Yellowdog Updater Modified.
This article explains 15 most frequently used yum commands with examples.
8Which package does a file belong to? – Use yum provides
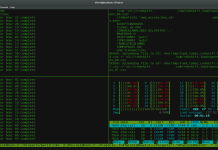
Use ‘yum provides’ if you like to know which package a particular file belongs to. For example, if you like to know the name of the package that has the /etc/sysconfig/sshd file, do the following.
root@yum ~]# yum provides /etc/sysconfig/sshd openssh-server-7.4p1-11.el7.x86_64 : An open source SSH server daemon Repo : base Matched from: Filename : /etc/sysconfig/sshd openssh-server-7.4p1-12.el7_4.x86_64 : An open source SSH server daemon Repo : updates Matched from: Filename : /etc/sysconfig/sshd openssh-server-7.4p1-13.el7_4.x86_64 : An open source SSH server daemon Repo : updates Matched from: Filename : /etc/sysconfig/sshd openssh-server-7.4p1-13.el7_4.x86_64 : An open source SSH server daemon Repo : @updates Matched from: Filename : /etc/sysconfig/sshd