In Unix- Linux , the name of the
In Unix- Linux , the name of the tar command is short for tape archiving, the storing of entire file systems onto magnetic tape, which is one use for the command. However, a more common use for tar is to simply combine a few files into a single file, for easy storage and distribution.
The tar command used to rip a collection of files and directories into highly compressed archive file commonly called tarball or tar, gzip and bzip in Unix – Linux. The tar is most widely used command to create compressed archive files and that can be moved easily from one disk to another disk or machine to machine.
3. Create tar.bz2 Archive File
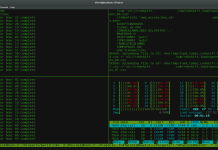
The bz2 feature compress and create archive file less than the size of the gzip. The bz2 compression takes more time to compress and decompress files as compared to gzip which takes less time. To create highly compressed tar file we use option as j. The following example command will create a emrepic.tar.bz2 file for a directory /emre . (Note: tar.bz2 and tbz is similar as tb2).
[root@cent ~]# tar cvfj emrepic.tar.bz2 emre emre/ emre/emrepics1.jpg emre/emrepics2.jpg emre/emrepics3.jpg emre/emrepics4.jpg [root@cent ~]# ls -l total 4 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 195 Mar 21 11:57 emre -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 222 Mar 21 12:15 emrepic.tar.bz2