Containers are a method of operating system virtualization that allow you to run an application and its dependencies in resource-isolated processes and Containers are a solution to the problem of how to get software to run reliably when moved from one computing environment to another.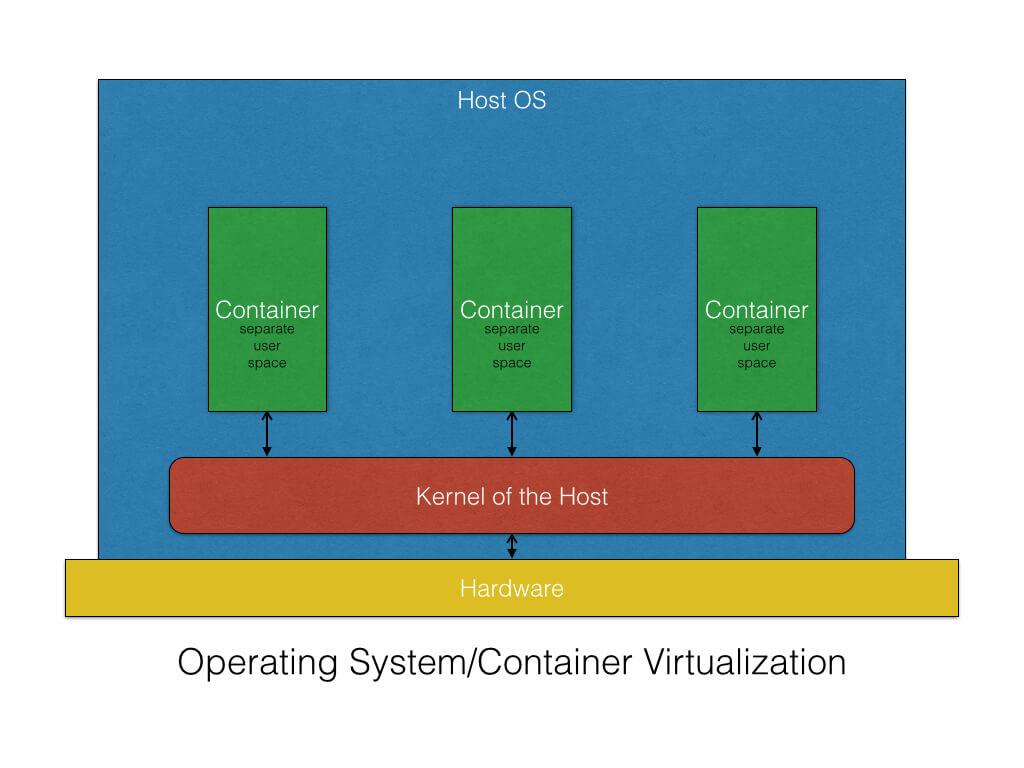
Its lightweight OS-level virtualizations that allow us to run an application and its dependencies in a resource-isolated process.
Difference Between Virtual Machines and Containers
Virtual machines generally include entire operating system along with the application. They also need a hypervisor running along with them to control the VM.
As they include the operating system, therefore their size is of several gigabytes. One of the downsides of using VMs is that they take up several minutes to boot up the OS, and they initialize the application they are hosting. At the same time, the containers are lightweight and are, mostly, in the megabytes size range. Comparing their performance to VMs, containers perform much better and can start almost instantly.
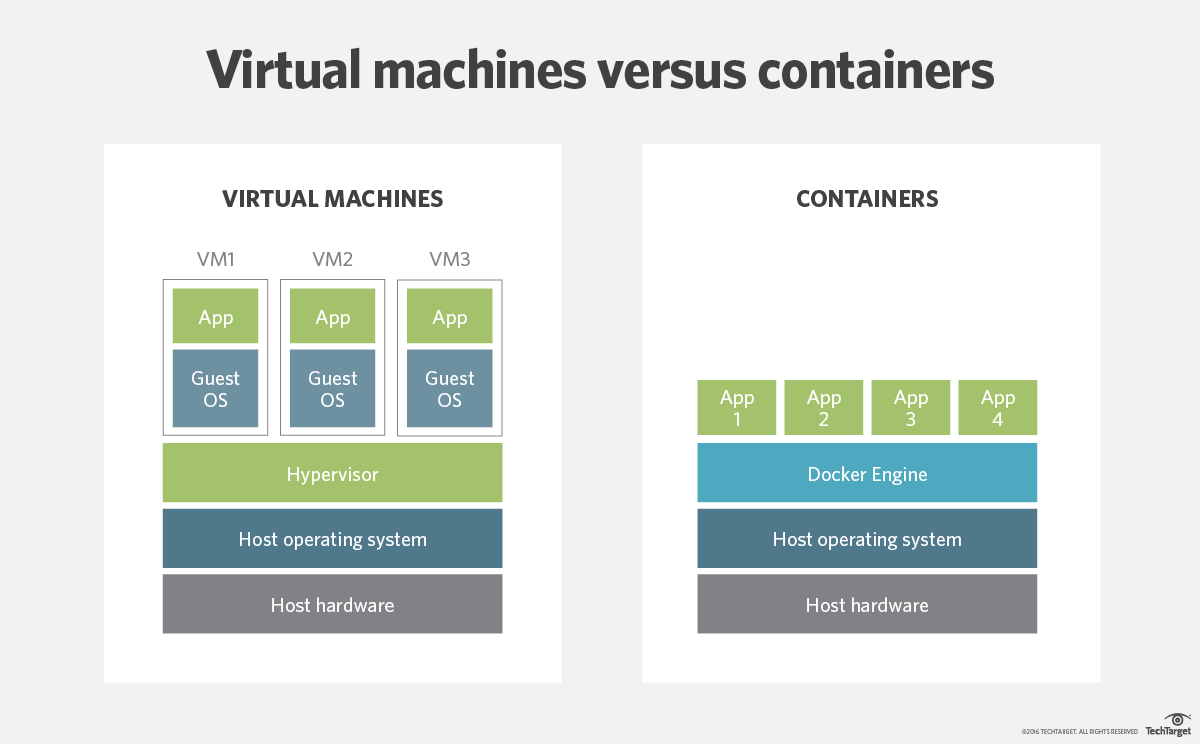
The benefits of containers often derive from their speed and lightweight nature; many more containers can be put onto a server than onto a traditional VM. Containers are “shareable” and can be used on a variety of public and private cloud deployments, accelerating dev and test by quickly packaging applications along with their dependencies. Additionally, containers reduce management overhead.