What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes is an open source platform that automates Linux container operations.
Why do we need a container cluster structure?
When you bring your applications in a containerized way, the task of high availability, scaling, auto deployment, service discovery, rollback, etc. You can easily do things like.But if you try to manage them separately, things can get out of control. At this point we need a container cluster structure.From an operational point of view, you can easily manage the work that n people will do at the moment.
Kubernetes Architecture
Kubernetes basically consists of masters and minions. This minion runs on the node in your applications called pods.Pods controlled by deployments.This structure communicates with a network that we call overlay in itself.Architecture is like below;
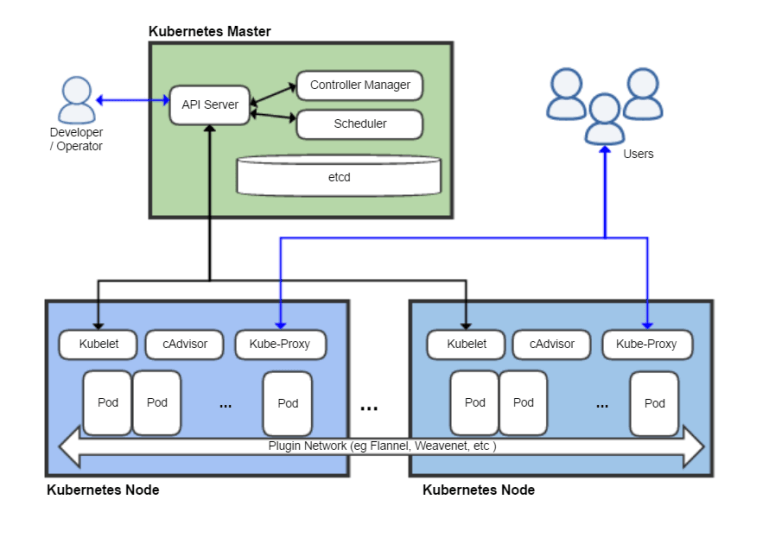
Pods:Container is a pod in the area where containers work.You can run one or more containers in a pod.The best practice; you should run one container in one pod.When the pod dies, it does not get back up again, so a new pod appears instead of the same image.
ReplicaSet:You can specify how many pods will be replicaSet.You can scale a pod to any size you want, without interruption.Kubernetes automatically distributes pods according to the suitability of the nodes.
Namespace: By inserting Namespace you can isolate and isolate one of your environments.
Service: The layer located at the front of the Service pods, which meets incoming requests and sends back to the pods.
Ingress: In front of all k8s services url redirection, load balancing, ssl termination etc. a web server where you can manage transactions from a single point; You can choose Nginx or Haproxy for the ingress.
Secret: You will store information such as password, user, token securely in the field.You can use it in your application with the name you give the information you store here.
ConfigMap: You can think like a key value database. You can keep your configs here and use them in your applications.
AutoScaling: With the Replication Controller, you can scale your work horizontally according to the metrics of the pods, such as CPU and memory. You can collect these metrics with heapster.
How can I make the monitoring section?
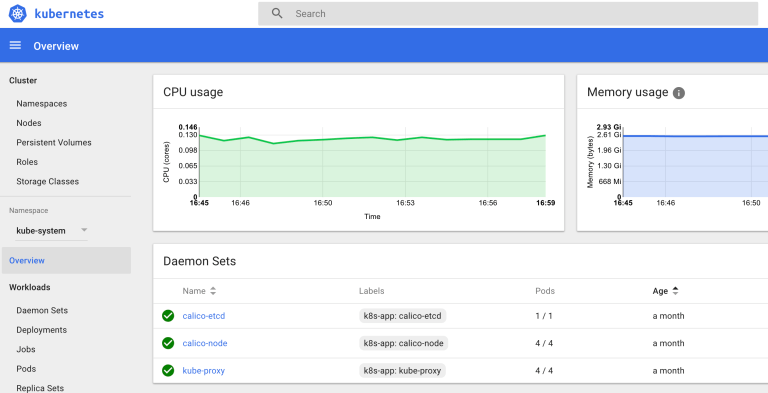
You can see Dashboard setup and Heapster and metrics. Besides this you can monitor with Influxdb and Grafana.
Finally
I tried to explain Kubernetes in general terms. I plan to make more detailed examples in my next post. See you soon.