Installing, removing, and updating packages is a typical activity on Linux. Most of the Linux distributions provides some kind of package manager utility. For example, apt-get, dpkg, rpm, yum, etc.
On some Linux distributions, yum is the default package manager.
Yum stands for Yellowdog Updater Modified.
This article explains 15 most frequently used yum commands with examples.
2Uninstall a package using yum remove
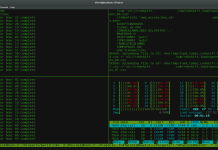
To remove a package (along with all its dependencies), use ‘yum remove package’ as shown below.
[root@yum emre]# yum remove wget -y Resolving Dependencies --> Running transaction check ---> Package wget.x86_64 0:1.14-15.el7_4.1 will be erased --> Finished Dependency Resolution Dependencies Resolved ================================================================================================================= Package Arch Version Repository Size ================================================================================================================= Removing: wget x86_64 1.14-15.el7_4.1 @rhui-rhel-7-server-rhui-rpms 2.0 M Transaction Summary ================================================================================================================= Remove 1 Package Installed size: 2.0 M Downloading packages: Running transaction check Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded Running transaction Erasing : wget-1.14-15.el7_4.1.x86_64 1/1 Verifying : wget-1.14-15.el7_4.1.x86_64 1/1 Removed: wget.x86_64 0:1.14-15.el7_4.1 Complete!