Installing, removing, and updating packages is a typical activity on Linux. Most of the Linux distributions provides some kind of package manager utility. For example, apt-get, dpkg, rpm, yum, etc.
On some Linux distributions, yum is the default package manager.
Yum stands for Yellowdog Updater Modified.
This article explains 15 most frequently used yum commands with examples.
3Upgrade an existing package using yum update
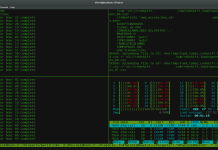
If you have a older version of a package, use ‘yum update package’ to upgrade it to the latest current version. This will also identify and install all required dependencies.
[root@yum ~]# yum update google-cloud-sdk Resolving Dependencies --> Running transaction check ---> Package google-cloud-sdk.noarch 0:193.0.0-1.el7 will be updated ---> Package google-cloud-sdk.noarch 0:194.0.0-1.el7 will be an update --> Finished Dependency Resolution Dependencies Resolved ================================================================================================================= Package Arch Version Repository Size ================================================================================================================= Updating: google-cloud-sdk noarch 194.0.0-1.el7 google-cloud-sdk 22 M Transaction Summary ================================================================================================================= Upgrade 1 Package Total download size: 22 M Is this ok [y/d/N]: y Downloading packages: Delta RPMs disabled because /usr/bin/applydeltarpm not installed. 3a6f297621cf6568b6c323c902803e0f4b138001ec27313c022fa867d5dabb2e-google-cloud-sdk-194.0.0 | 22 MB 00:00:01 Running transaction check Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded Running transaction Updating : google-cloud-sdk-194.0.0-1.el7.noarch 1/2 Cleanup : google-cloud-sdk-193.0.0-1.el7.noarch 2/2 Verifying : google-cloud-sdk-194.0.0-1.el7.noarch 1/2 Verifying : google-cloud-sdk-193.0.0-1.el7.noarch 2/2 Updated: google-cloud-sdk.noarch 0:194.0.0-1.el7 Complete!